
| Scientific name | Monodora myristica |
| Common names | Guinea pepper, Negro pepper, Ethiopian pepper etc. |
| Common name | Calabash nutmeg |
| Local names | |
| Family | Annonaceae |
| Description | Tree or shrub 3.6-30m tall, with trunk up to 1m in diameter fissured at the base, bark grey, vertically corrugated with rounded ridges. |
| Habitat | A tropical shrub of the Annonacece or custard apple family of flowering plants. |
| Part used | |
| Season | |
| Active ingredients | |
| Uses | Used as spice and condiment. The root is chewed to relieve toothaches and athritis. The seeds are used to relieve anemia, haemorrhids, sexual weakness, and wounds. |

| Scientific name | Aframomum meleguet |
| Common names | Grains of paradise, Alligator pepper and melegueta pepper |
| Common name | |
| Local names | Fam wusa (Twi), Ataku (Ewe) |
| Family | Zingiberaceae |
| Description | A tufted leafy herbaceous plant up to 2m high, leaves are distichously arranged etc. |
| Habitat | It is cultivated in forest regions in farms and home gardens. Its matured dried fruit and seeds are sold in the markets. |
| Part used | |
| Season | |
| Active ingredients | Oleoresins (volatile oil contains paradols, gingerols and shogaols). |
| Uses | it is an aromatic stimulant, for treatment of coughs and bronchitis, anti-rheumatic, for dyspepsia, also used as an adjuvant. Used in Japan as aphrodisiac. |
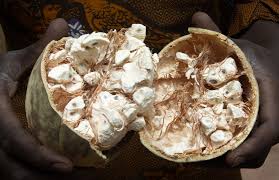
| Scientific name | Adansonia digitata |
| Common names | |
| Common name | Baobab |
| Local names | Adzido (Ewe), alagbatsi, Télou (Tem, Kotokoli) |
| Family | Bombacaceae |
| Description | It is a big savannah tree growing up to 30m with trunk base. |
| Habitat | It is found in hot, dry savannah growing in solitary individualism. |
| Part used | Bark, fruit pulp, seed, leaves. |
| Season | |
| Active ingredients | Has twice much calcium as milk, antioxidants, iron and potassium, has 6times the vitamin C of an orange, sugars. |
| Uses | The leaves are potherbs and eaten as relish. Fruit used as beverage. Seed produce edible oil. Baobab fruit used as ingredient in smoothies and cereal bars Bark |

| Scientific name | Maytenus senegalensis |
| Common names | |
| Common name | |
| Local names | Claromapka (Ewe), fõtchõvõwou (Tem, Kotokoli) |
| Family | Celastraceae |
| Description | It can reach a height of 16 meters The trunk is straight, the tree can go up to 16 meters, the branches are flexible, drooping, red or gray-green, and the bark gray, hard, thick and grooved vertically. It can be thorny, the thorns then from 1 to 5 cm. Its oval, flexible and fleshy leaves are 3 to 12 cm long with a generally pink central vein. They are either grouped or alternate. The peduncle is short. The fragrant flowers are creamy white and densely cover the tree. They give green, then red, round fruits up to 6 mm in diameter. These fruits give 1 seed of a shiny brown red, half are covered with a soft white aril. |
| Habitat | It is present in North Africa, from Somalia to Senegal, in South Africa and Madagascar, in the Canary Islands, as well as in the extreme south of the Iberian Peninsula. |
| Part used | Leaves, bark, fruit, seeds, roots |
| Season | |
| Active ingredients | |
| Uses | It is used as firewood, charcoal, fodder (leaves), living or dry defense (thorny branches), roofing material for local dwellings. From a drug perspective, leaves, bark, fruit, seeds, roots are use in decoction, powder or juice for treatment of injuries, diarrhea, cough, cold, sore throat, … |
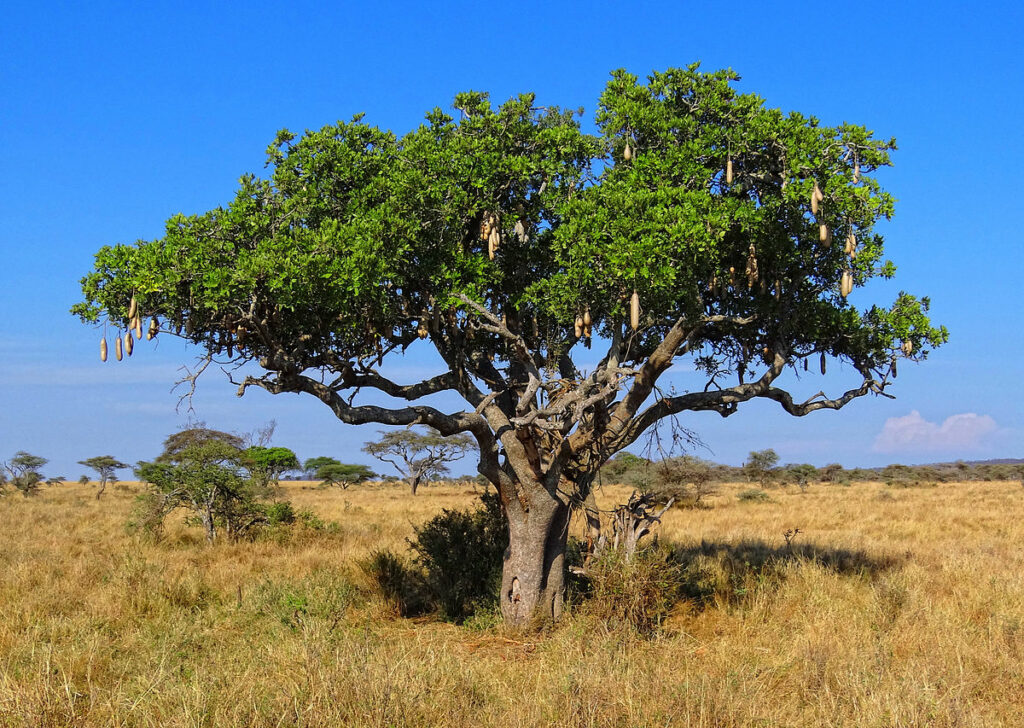

| Scientific name | Kigelia africana |
| Common names | |
| Common name | Sausage tree |
| Local names | Nufuten |
| Family | Bignoniaceae |
| Description | It is a short, squat trunk, has light brown, sometimes flaky bark and supports a dense rounded to spreading crown (18m high) etc. |
| Habitat | It is found near riverbanks and a times planted on roadside. |
| Part used | |
| Season | |
| Active ingredients | Iridoids and naphthoquinones: Naphthoquinones (including kigelinone). Monoterpenoids – nepthaquinones (pinnata), isocoumarins (including kigelin), lignans (kigeliol), sterols (including bêta-sitosterol and stigmaterol), and flavonoids (including quercetin and luteolin) |
| Uses | Folkore (Uses): Rheumatism, snakebites, evil spirits, and even tornadoes. Used in making alcoholic beverage similar to beer, fresh fruit poisonous and strongly purgative; fruits are prepared for consumption by drying, roasting or fermentation. It is an ornamental tree. Orthodox (Uses): Anti-inflammatory, skin ailments, from fungal infections, boils, psoriasis, and eczema, leprosy, Syphilis and Skin Cancer. It has also internal application including the treatment of dysentery, tapeworm, ringworm, post-partum hemorrhaging, diabetes, malaria, pneumonia and toothache. The leaves are important livestock fodder. Fruit is aphrodisiac. |
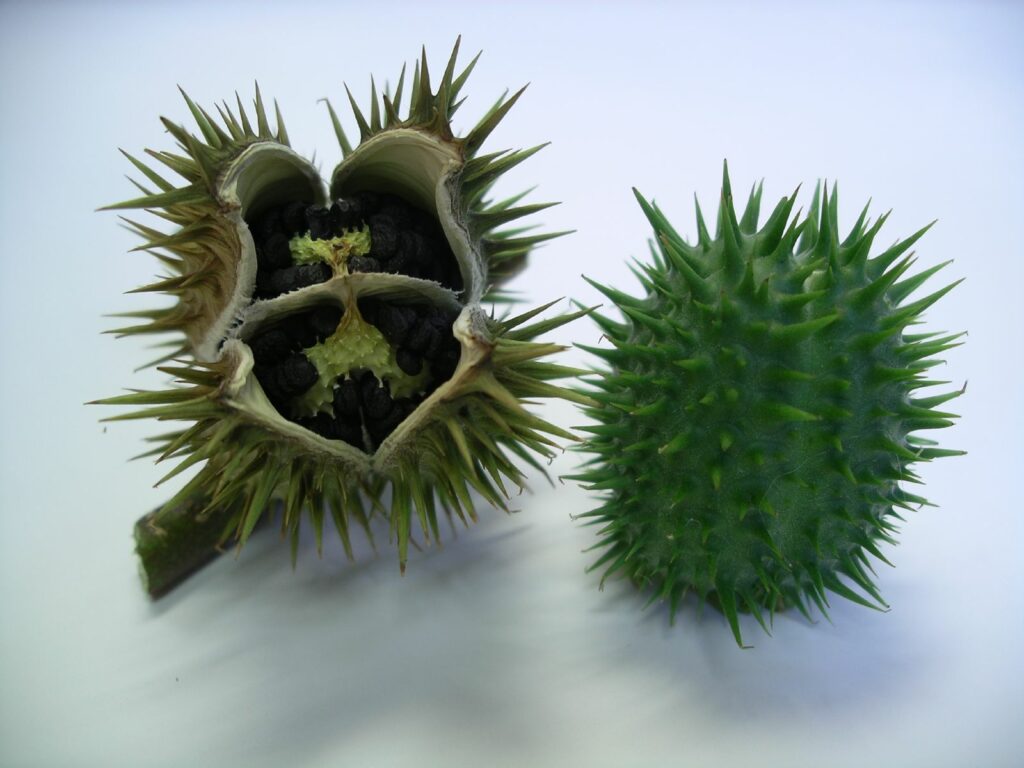

| Scientific name | Datura stramonium |
| Common names | Thorn apple, Jimson weed |
| Common name | Thorn apple |
| Local names | |
| Family | Solanaceae |
| Description | |
| Habitat | |
| Part used | |
| Season | |
| Active ingredients | Tropane alkaloids, hyoscyamine and scopolamine |
| Uses | Used as hallucinogen |

| Scientific name | Physostigma venenosum |
| Common names | |
| Common name | Calabar Beans |
| Local names | |
| Family | Papilionaceae |
| Description | |
| Habitat | |
| Part used | Seed |
| Season | May – June |
| Active ingredients | Tropane alkaloids, hyoscyamine and scopolamine |
| Uses | Controls glaucoma, Adie’s syndrome, Mana Myasthenia Gravis.lmproves Memory in Alzheim disease. It serves as antidote to atropine poisoni and other anti- depressant |

| Scientific name | Zingiber officinale |
| Common names | |
| Common name | Ginger |
| Local names | Dote (Ewe), Atarara (Tem, Kotokoli) |
| Family | Zingiberaceae |
| Description | Ginger is a tropical herbaceous perennial about 0.90 m tall from a rhizome. The evergreen leaves are lanceolate, bier, long and fragrant. The flowers are white and yellow, punctuated with red on the lips, the bracts are green and yellow. Fresh and Sun Dried ginger |
| Habitat | It is found in tropical zone |
| Part used | rhizome |
| Season | All the year |
| Active ingredients | |
| Uses | Used as spice in food, drunk as juice. From a drug perspective, ginger shows antiemetic properties. It is used for motion sickness, postoperative nausea, to protect gastric mucosa. It lowers cholesterol, blood triglycerides, fatty acids and phospholipids |
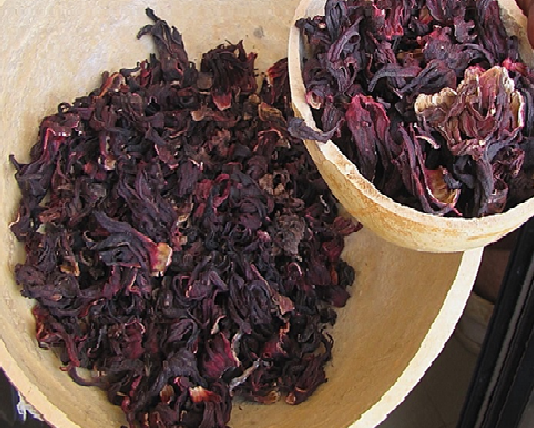

| Scientific name | Hibiscus sabdariffa |
| Common names | Hibiscus, Sudanese rose, roselle, bissap |
| Common name | |
| Local names | Sooboro, bissap |
| Family | Malvaceae |
| Description | it is an annual or perennial herb or wood based sub-shrub, growing to 2-2.5m tall, the leaves are deeply three to five-lobed etc. |
| Habitat | cultivated in the savannahs in the North of Togo and Burkina Faso. |
| Part used | Flowers |
| Season | July – October |
| Active ingredients | It contains around 49 calories 1.9 protein, a total of 12.3g carbohydrates, 14mg ascorbic acid and many other organic compounds. Vitamin C, anthocyanins, protocatechuic acid, flavonoids (gossypetin, hibiscetine and sabdaretine, daphniphylline. Small amount of myrtillin, chrysanthenin and delphinidin. |
| Uses | Folklore (Uses): diuretic, mild laxative, for treatment of cardiac and nerve diseases and cancer. Orthodox (Uses): Treats hypertension and urinary tract infections, beneficial to the principal organs of the human body. These are the cardiovascular, nervous and the digestive system including the kidney. It is useful in, Arteriosclerosis as an intestinal antiseptic. Seeds are aphrodisiac. The leaves are medicinally emollient used as diuretic, refrigerant and sedative. It again strengthens the body’s defensive capability against negative influences promoting metabolism and destroying most disease prone micro-organisms. It could be used as natural dewormer. As a tea beverage, the addition of critic acid or lemon results in obtaining a pleasant taste and stimulating the production of Bile that helps the liver to perform its digestive functions. |

| Scientific name | Cola nitida |
| Common names | |
| Common name | Cola nuts |
| Local names | Goro (Ewe, Tem, Kotokoli) |
| Family | Sterculiaceae |
| Description | The cola nut tree is an evergreen tree cultivated in the forest and high savannah areas. It takes between 7 to 8 years to fruit. |
| Habitat | Could be found in the wild in the forest and high savannah. |
| Part used | Nut |
| Season | October – February |
| Active ingredients | |
| Uses | The kola nut has a bitter flavor and contains caffeine. It is chewed in many West African cultures, individually or in a group setting. It is often used ceremonially, presented to tribal chiefs or presented to guests. It is preferred among African Muslims, who are forbidden to drink alcohol. Chewing kola nut can ease hunger pangs. Frequent chewing of the kola nut can also lead to stained teeth. Among the urban youth of West Africa, kola nut is becoming less popular. Outside mainland Africa, some species are cultivated for their nuts in Brazil, Jamaica and elsewhere in the humid tropics. Kola nuts are often used to treat whooping cough and asthma. The caffeine present acts as a bronchodilator, expanding the bronchial air passages. Kola nuts are perhaps best known to Western culture as a flavoring ingredient and one of the sources of caffeine in cola and other similarly flavored beverages. |

| Scientific name | Moringa oleifera |
| Common names | |
| Common name | Horse Raddish Tree |
| Local names | |
| Family | Moringaceae |
| Description | |
| Habitat | |
| Part used | Leaves, seed, bark, roots |
| Season | All year |
| Active ingredients | Pterigospermine |
| Uses | Broad-spectrum medicine for almost 300 ailments including Hypertension, Impotence, Asthma, Cardiovascular disease, all forms of Malaria headaches etc. |
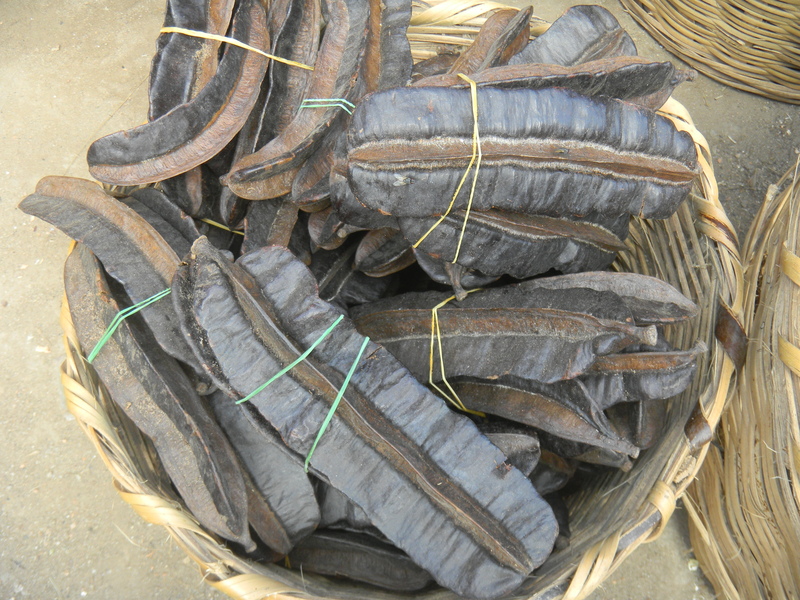

| Scientific name | Tetrapleura tetraptera |
| Common names | |
| Common name | Aridan |
| Local names | Prekese |
| Family | Mimosaceae |
| Description | A deciduous tree 6-30m high, bark smooth to rather rough, grey or brown, young branchlets glabrous with petiole leaves. |
| Habitat | It is found in river rain and secondary forests. |
| Part used | Fruit, bark, leaves, pulp, roots etc. |
| Season | |
| Active ingredients | Rich in sugars, tannins, coumarin, scopoletin, aridanin, magnesium, potassium, iron, phosphorus, Vitamin C etc. |
| Uses | Folklore or Traditional uses: Therapeutically useful in the management of convulsion, leprosy inflammation and rheumatoid pains. It is a spice; treats diabetes, hypertension, arthritis etc. Orthodox (Use): It has anti-inflammatory and hypoglycemia properties. It controls cholesterol levels. Controls hypertension Treat Bilharzia Enhances healing of production of breast milk. Enhances healing reproductive wounds. Scent used as perfume. It is used as condiment. Flavor in beverages. |

| Scientific name: | Capsicum Frutescens |
| Common names | |
| Common name | |
| Local names | |
| Family | Solanaceae |
| Description | |
| Habitat | |
| Part used | |
| Season | |
| Active ingredients | |
| Uses |

| Scientific name | Okoubaka aubrevillei |
| Common names | |
| Common name | Okoubaka |
| Local names | |
| Family | Santalaceae |
| Description | The okoubaka tree is considered a trophophyte, meaning it is adapted to an environment that alternates between periods of heavy rainfall and droughts. It is deciduous meaning it sheds its leaves seasonally, and monoecious, meaning it contains both male and female reproductive flower parts. It is a tree that can reach 40 meters in height with a trunk that can reach 3 meters in width. The tree forms a large bushy crown and has a straight and cylindrical bole (trunk). Its bark is course and usually reddish-brown. The tree development fits the Mangenot architectural model. |
| Habitat | |
| Part used | Seeds, Bark |
| Season | |
| Active ingredients | |
| Uses | The tree is used for various medicinal purposes such as anti-malarial drugs. |

| Scientific name | Mucuna pruriens / Mucuna flagellipes |
| Common names | |
| Common name | |
| Local names | Eve (Ewe) |
| Family | Fabaceae |
| Description | The plant is an annual climbing shrub with long vines that can reach over 15 metres (50 ft) in length. When the plant is young, it is almost completely covered with fuzzy hairs, but when older, it is almost completely free of hairs. The leaves are tripinnate, ovate, reverse ovate, rhombus-shaped or widely ovate. The sides of the leaves are often heavily grooved, and the tips are pointy. In young M. pruriens plants, both sides of the leaves have hairs. The stems of the leaflets are two to three millimeters long (approximately one tenth of an inch). Additional adjacent leaves are present and are about 5 millimetres (0.2 in) long. |
| Habitat | |
| Part used | Seed |
| Season | |
| Active ingredients | The seeds of the plant contain L-DOPA, with trace amounts of serotonin, nicotine, and bufotenine. |
| Uses | The seeds of Mucuna pruriens have been used for treating many dysfunctions in Tibb-e-Unani (Unani Medicine). It is also used in Ayurvedic medicine. The plant and its extracts have been long used in tribal communities as a toxin antagonist for various snakebites. It has been studied for its effects against bites by Naja spp. (cobra), Echis (Saw scaled viper), Calloselasma (Malayan Pit viper) and Bangarus (Krait). It has long been used in traditional Ayurvedic Indian medicine in an attempt to treat diseases including Parkinson’s disease. It has been investigated in low income regions of the world as an alternative treatment for Parkinson’s disease due to its high content of L-dopa. Mucuna prurien seeds have been recognized for their ability to significantly alleviate neurotoxocity induced by Parkinson’s disease. Dried leaves of M. pruriens are sometimes smoked. |